Forge Code Integration
Overview
Forge Code is an AI-powered shell assistant that brings intelligent coding capabilities directly to your terminal. Unlike IDE-specific tools, Forge works seamlessly with any development environment, making it the perfect companion for developers who value their existing workflow.
Key Features
- Terminal-Native: Works in your shell without requiring a specific IDE
- Model Agnostic: Supports 300+ models including RelaxAI, OpenAI, Anthropic Claude, and local models
- Privacy-First: All code stays on your machine with your own API keys
- Zero IDE Lock-in: Compatible with VS Code, Neovim, IntelliJ, Xcode, or any editor
- Git-Aware: Understands your entire codebase and version history
- Custom Workflows: Create and share specialized agents for different tasks
Use Cases
- Understanding complex codebases and legacy code
- Implementing new features with natural language descriptions
- Debugging issues and finding root causes
- Performing large-scale refactors and migrations
- Generating tests and documentation
- Answering questions about code architecture and data flow
Use Case
Perfect for developers who prefer working in the terminal and want AI assistance without switching contexts or learning new IDEs.
Setup Instructions
-
Install Forge globally using npm:
Terminal window npm install -g forgecode@latest -
Create a
.envfile in your home directory with the following configuration:Terminal window # API Configuration for RelaxAIOPENAI_API_KEY=RELAX_API_KEYOPENAI_URL=https://api.relax.ai/v1 -
Configure Forge to use RelaxAI by running:
Terminal window npx forgecode@latest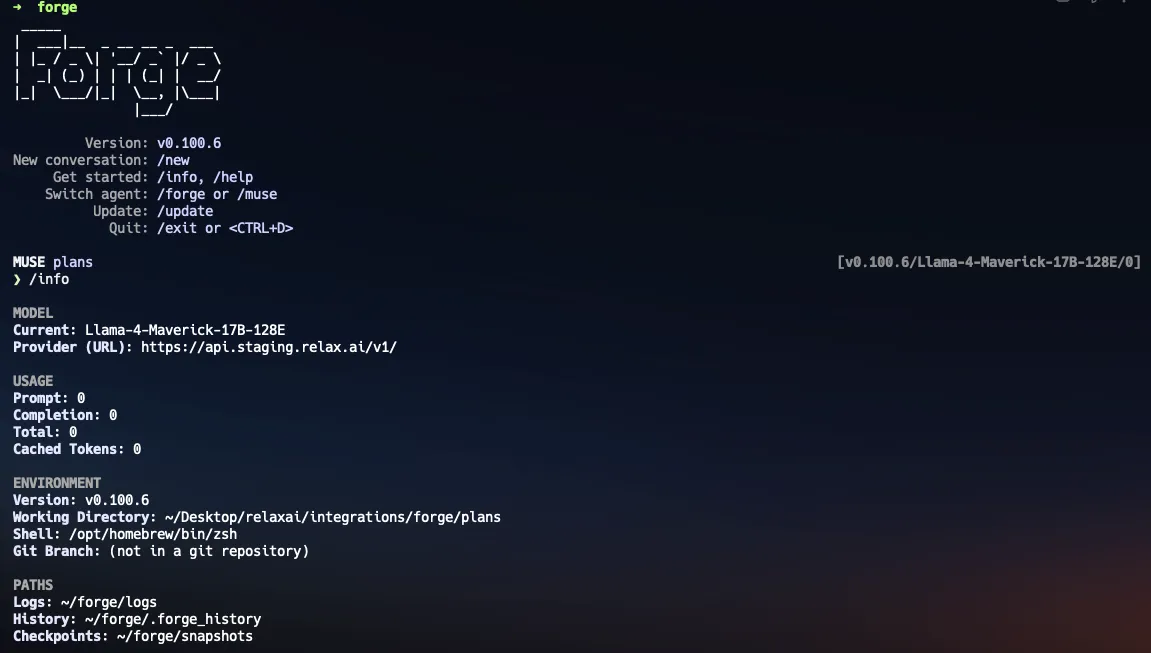
-
Select the model from the list of available models. You can use RelaxAI models like
Llama-4-Maverick-17B-128Eor any other compatible model.
❯ /model? Select a model:DeepSeek-R1-0528Mistral-7b-embedding➤ Llama-4-Maverick-17B-128EDSE-QWen2-2b-MRL-V1[Type a name or use arrow keys to navigate and Enter to select]- Start using Forge in your terminal by tying in any natural language command, or experiment with the interactive agents. Please refer to the Forge Commands for more details on available commands and configurations.
# forge shell> "Implement a new feature that allows users to export data in CSV format"- You can also create custom workflows by defining agents in the
forge.yamlfile in your project root. This allows you to tailor Forge’s behavior to your specific development needs. An example command to use themuseagent for planning and implementing a feature:
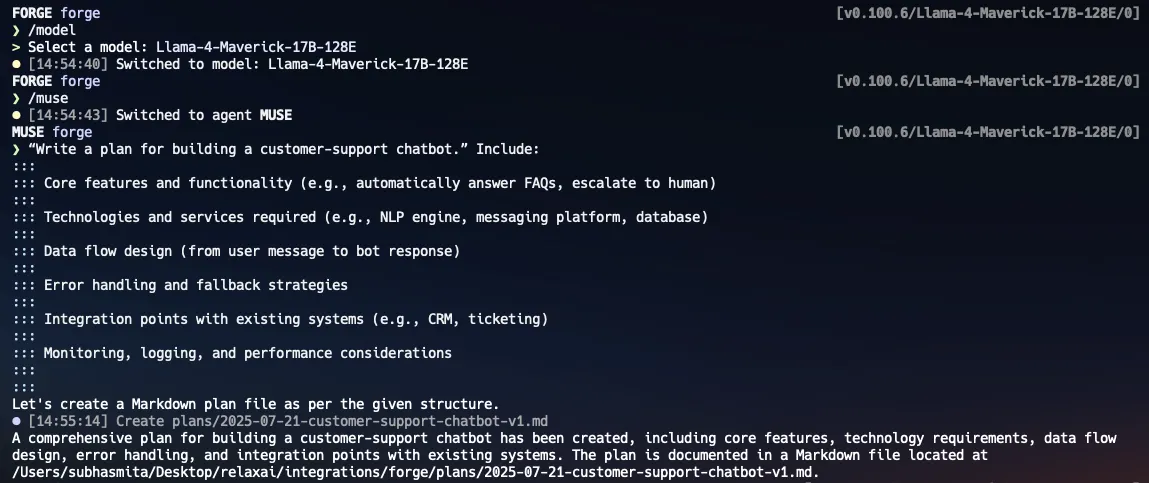
Commands and Usage
Forge provides both built-in commands and natural language interaction:
Built-in Commands:
- /new - Start a new task with fresh context
- /info - View environment summary and configuration details
- /model - Select and set a specific AI model
- /agent - Switch between available agents
- /forge - Switch to Forge Agent (full execution capabilities)
- /muse - Switch to Muse Agent (read-only analysis mode)
- /dump - Save current conversation in JSON format
Shell Commands: Execute native shell commands directly by prefixing with !:
- !ls -la - List files
- !python script.py - Run scripts
Natural Language Interaction: Simply type your requests in natural language:
- “Explain this function and how it works”
- “Debug this error message…”
- “Refactor this code to improve…”
Advanced Features:
Agent Modes: Switch between Forge (execution) and Muse (analysis) agents Context Understanding: Automatically analyzes your project structure Git Integration: Understands code history and changes Multi-file Operations: Handle complex changes across multiple files
Best Practices
- Keep your prompts clear and specific for best results
- Use Forge for complex tasks that benefit from codebase understanding
- Review generated code before committing
- Create custom workflows for repetitive tasks
- Leverage git integration for understanding code evolution
Troubleshooting
- Connection Issues: Verify your API endpoint and key in the .env file
- Slow Responses: Consider using a faster model or adjusting max_tokens
- Context Errors: Try reducing the scope of your request or breaking it into smaller tasks