Dify Integration
Overview
Dify is an open-source platform for developing production-ready LLM applications. It provides an intuitive interface that combines agentic AI workflows, RAG pipelines, agent capabilities, model management, and observability features. With its visual workflow builder and comprehensive model support, Dify enables rapid prototyping and deployment of AI applications without extensive coding.
Perfect for teams wanting to rapidly prototype and deploy AI applications with a visual interface while maintaining the flexibility to integrate custom models and workflows.
Key Features
- Visual Workflow Builder: Drag-and-drop interface for creating complex AI workflows
- Comprehensive Model Support: Seamless integration with 100+ LLMs including OpenAI-compatible APIs
- RAG Pipeline: Built-in document processing and retrieval capabilities
- Agent Framework: Create autonomous AI agents with custom tools and capabilities
- Prompt IDE: Test and optimize prompts with model comparison features
- Multi-tenant Architecture: Enterprise-ready with team collaboration features
- API-First Design: RESTful APIs for all features enabling programmatic access
Use Cases
- Build conversational AI applications and chatbots
- Create AI-powered workflow automation systems
- Develop RAG-based knowledge management solutions
- Prototype and test AI applications before production deployment
- Build multi-agent systems for complex task automation
- Create custom AI assistants with specific domain knowledge
System Requirements
Before installation, ensure your system meets these minimum requirements:
- CPU: 2 Core
- RAM: 4 GB minimum
- Storage: 10 GB free disk space
- Docker: 20.10.17 or later
- Docker Compose: 2.2.3 or later
Docker Installation
-
Clone the Dify repository with the latest stable release:
Terminal window git clone --branch "$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/langgenius/dify/releases/latest | jq -r .tag_name)" https://github.com/langgenius/dify.git -
Navigate to the Docker directory:
Terminal window cd dify/docker -
Copy the environment configuration file:
Terminal window cp .env.example .env -
Edit the
.envfile to customize your deployment:Terminal window # Core Service ConfigurationCONSOLE_API_URL=http://localhostSERVICE_API_URL=http://localhost/apiAPP_WEB_URL=http://localhost# Security - Change these in production!SECRET_KEY=your-secret-key-hereINIT_PASSWORD=your-admin-password# Database ConfigurationDB_USERNAME=postgresDB_PASSWORD=difyai123456DB_HOST=dbDB_PORT=5432DB_DATABASE=dify# Redis ConfigurationREDIS_HOST=redisREDIS_PORT=6379REDIS_PASSWORD=difyai123456# Vector Store (options: weaviate, qdrant, milvus, pgvector)VECTOR_STORE=weaviate -
Start Dify using Docker Compose:
Terminal window docker compose up -d -
Verify all services are running:
Terminal window docker compose psYou should see 11 services running including:
- Core Services: api, worker, web
- Dependencies: db, redis, nginx, weaviate, sandbox, ssrf_proxy
-
Access the initialization page to set up admin account:
http://localhost/install
RelaxAI Integration Setup
-
Log in to Dify and navigate to Settings → Model Provider
-
Click on OpenAI-API-compatible provider
-
If not installed, click Install Plugin when prompted
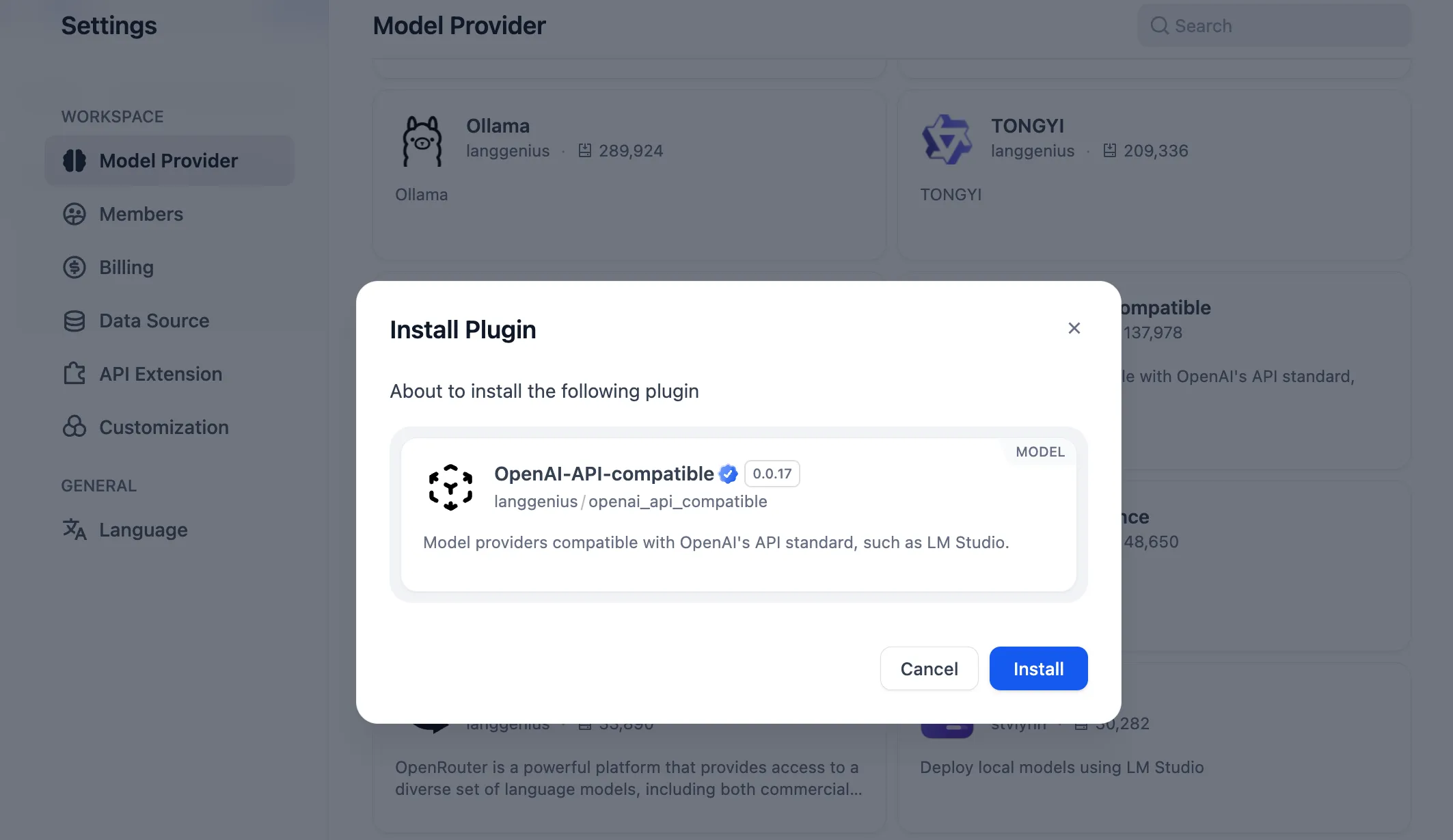
-
Configure the OpenAI-compatible provider with RelaxAI settings:
- Base URL:
https://api.relax.ai/v1 - API Key:
RELAX_API_KEY
- Base URL:
-
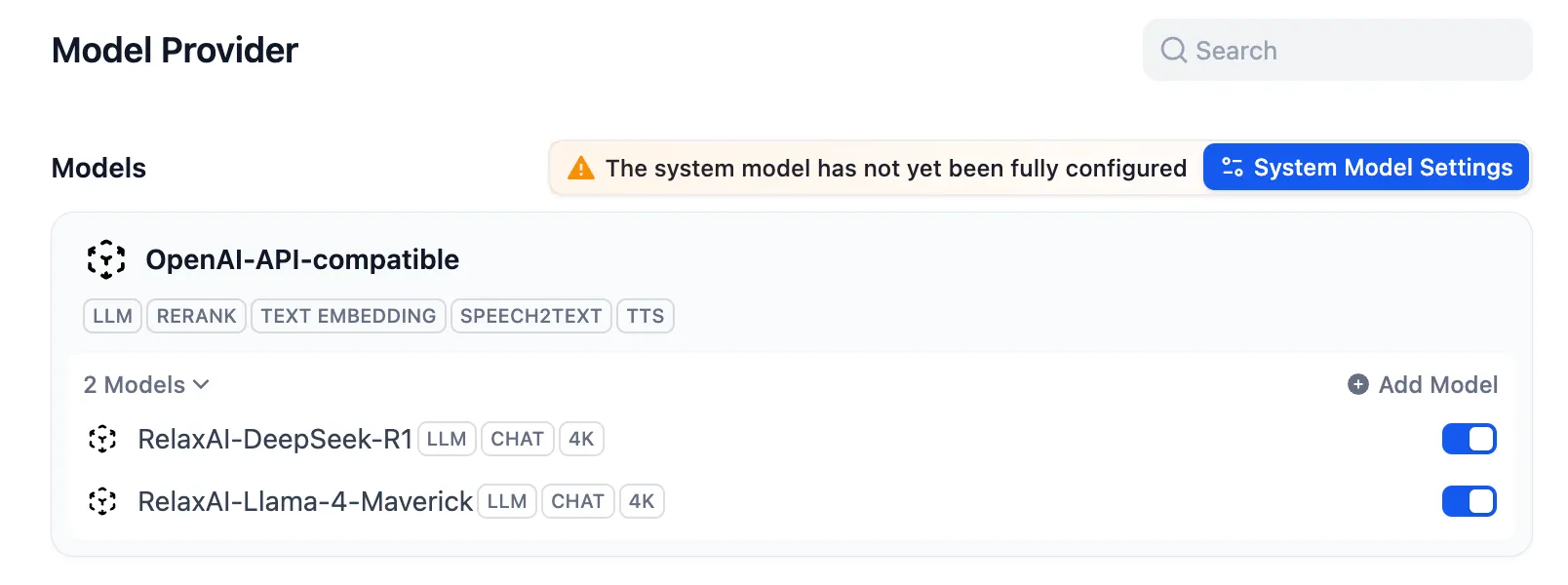
Add RelaxAI models by clicking Add Model and configuring:
Model Name: RelaxAI-Llama-4-MaverickModel ID: Llama-4-Maverick-17B-128EType: LLMCapabilities: [CHAT]Context Length: 4096Max Tokens: 4096 -
For additional models like DeepSeek-R1:
Model Name: RelaxAI-DeepSeek-R1Model ID: DeepSeek-R1-0528Type: LLMCapabilities: [CHAT]Context Length: 4096Max Tokens: 4096
Advanced Configuration
Custom Docker Compose Configuration:
For production deployments, modify docker-compose.yaml:
services: api: image: langgenius/dify-api:latest environment: # Scaling configuration GUNICORN_WORKERS: 4 CELERY_WORKER_AMOUNT: 2
# Performance tuning SQLALCHEMY_POOL_SIZE: 30 SQLALCHEMY_MAX_OVERFLOW: 60
# Security hardening WEB_API_CORS_ALLOW_ORIGINS: "https://your-domain.com" CONSOLE_CORS_ALLOW_ORIGINS: "https://your-domain.com"Vector Database Options:
Dify supports multiple vector stores. Configure in .env:
# Weaviate (default)VECTOR_STORE=weaviateWEAVIATE_ENDPOINT=http://weaviate:8080
# QdrantVECTOR_STORE=qdrantQDRANT_URL=http://qdrant:6333
# PGVectorVECTOR_STORE=pgvectorPGVECTOR_HOST=pgvectorPGVECTOR_PORT=5432SSL/HTTPS Configuration: For production, enable HTTPS:
# In .env fileNGINX_HTTPS_ENABLED=trueNGINX_SSL_PORT=443NGINX_SERVER_NAME=your-domain.com
# Certbot auto-renewal is includedWorkflow Development
Create AI workflows using Dify’s visual builder:
-
Create New App: Choose between Chat, Completion, or Workflow app types
-
Design Workflow:
- Add nodes: LLM, Knowledge Retrieval, Code Execution, HTTP Request
- Connect nodes to define data flow
- Configure each node with specific parameters
-
Integrate RelaxAI Models:
Node: LLMModel: RelaxAI-Llama-4-MaverickTemperature: 0.7Max Tokens: 2048System Prompt: "You are a helpful assistant..." -
Test and Debug: Use the built-in testing interface to validate workflows
-
Deploy: Get API endpoints for programmatic access
API Integration
Access Dify applications via API:
# Get API credentials from app settingsAPI_KEY="your-app-api-key"APP_ID="your-app-id"
# Chat completionscurl -X POST "http://localhost/v1/chat/completions" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "app_id": "'$APP_ID'", "query": "Hello, how can you help me?", "conversation_id": "optional-session-id" }'
# Workflow executioncurl -X POST "http://localhost/v1/workflows/run" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "app_id": "'$APP_ID'", "inputs": { "input_field": "value" } }'Performance Optimization
- Database Indexing: Ensure proper indexes on frequently queried columns
- Redis Configuration: Increase memory allocation for heavy caching needs
- Worker Scaling: Adjust CELERY_WORKER_AMOUNT based on workload
- Vector Store Optimization: Use dedicated vector database for large-scale RAG
- Model Caching: Enable model response caching for repeated queries
- Resource Limits: Set Docker resource constraints to prevent resource exhaustion
Monitoring and Observability
Monitor Dify deployment health:
# View logs for specific servicedocker compose logs -f api
# Monitor resource usagedocker stats
# Check service healthcurl http://localhost/health
# Access metrics (if enabled)curl http://localhost/metricsBackup and Recovery
Regular backup procedures:
# Backup databasedocker compose exec db pg_dump -U postgres dify > dify_backup_$(date +%Y%m%d).sql
# Backup volumestar -czf dify_volumes_$(date +%Y%m%d).tar.gz volumes/
# Restore databasedocker compose exec -T db psql -U postgres dify < dify_backup.sqlTroubleshooting
- Services not starting: Check port conflicts and ensure ports 80, 443, 5432, 6379 are available
- Model provider errors: Verify API credentials and endpoint URLs are correct
- Memory issues: Increase Docker memory allocation, minimum 4GB recommended
- Vector store connection failed: Ensure selected vector database service is running
- SSL certificate issues: Check Certbot container logs and domain configuration
- Slow performance: Scale worker instances and optimize database queries
- Container networking: Use
host.docker.internalfor host machine access
Best Practices
- Always use environment variables for sensitive configuration
- Regularly update to latest Dify version for security patches
- Implement proper backup strategies before production deployment
- Use dedicated vector database for production RAG applications
- Monitor resource usage and scale services accordingly
- Enable HTTPS for production deployments
- Implement rate limiting for public-facing APIs
- Use persistent volumes for data that needs to survive container restarts
Example Usage: Building a RAG-Powered Documentation Assistant
This section demonstrates how to build a sophisticated RAG system using Dify with RelaxAI models. We’ll create a documentation assistant that can answer questions with context-aware responses.
Step 1: Create Knowledge Base
- Navigate to Knowledge Section
- Log in to Dify dashboard
- Click “Knowledge” in the left sidebar
- Click “Create Knowledge”
-
Configure Knowledge Base
Name: Product DocumentationDescription: Technical documentation for our productPermission: Only me (or Team based on your needs) -
Upload Documents
- Click “Import” and select your files (PDF, TXT, MD, DOCX)
- Configure text processing:
Segmentation Settings:Mode: AutomaticChunk Size: 500 tokensChunk Overlap: 50 tokensPreprocessing Rules:- Remove extra spaces: Yes- Remove URLs/emails: No (keep for technical docs) -
Set Embedding Model
Embedding Model: Mistral-7b-embeddingVector Database: WeaviateRetrieval Settings:Top K: 5Score Threshold: 0.7
Step 2: Create Workflow Application
-
Create New App
- Go to “Studio” → “Create App”
- Select “Workflow” type
- Name: “Documentation Assistant”
-
Design the Workflow
Visual workflow structure:
[Start] → [Knowledge Retrieval] → [Context Processing] → [LLM Generation] → [Output] → [End] -
Configure Workflow Nodes
Start Node (Input):
Variables:- user_query:Type: StringRequired: trueDescription: "User's question"Knowledge Retrieval Node:
Node Type: Knowledge RetrievalKnowledge Base: Product DocumentationQuery: {{user_query}}Top K: 5Score Threshold: 0.7Reranking Model: RelaxAI-DeepSeek-R1Context Processing Node (Code):
def main(retrieved_docs, user_query):if not retrieved_docs:return {"context": "No relevant documentation found.", "has_context": False}formatted_context = []for idx, doc in enumerate(retrieved_docs[:3]):formatted_context.append(f"""Document {idx + 1}:Source: {doc.metadata.get('source', 'Unknown')}Content: {doc.content}---""")return {"context": "\n".join(formatted_context),"has_context": True,"source_count": len(retrieved_docs)}LLM Generation Node:
Node Type: LLMModel: RelaxAI-Llama-4-MaverickTemperature: 0.3Max Tokens: 1500System Prompt: |You are a helpful documentation assistant. Answer questions basedONLY on the provided context. If the context doesn't contain theanswer, say so clearly. Cite sources when referencing information.User Prompt: |Context: {{context}}Question: {{user_query}}Please provide a comprehensive answer based on the documentation.Output Formatting Node:
Node Type: TemplateTemplate: |## Answer{{llm_response}}---**Sources Consulted:** {{source_count}} documents
Step 3: Test the Application
- Run Test Queries
- Click “Preview” in the workflow editor and test with sample questions:
- “How do I configure authentication?”
- “What are the system requirements?”
- “How to troubleshoot connection errors?”
- Verify Responses
- Check accuracy against source documents
- Ensure proper source citation
- Validate handling of out-of-context questions
Step 4: Deploy and Integrate
-
Publish the Workflow
- Click “Publish” in the editor
- Navigate to “API Access”
- Copy API credentials
-
API Integration Example
import requestsclass DifyDocAssistant:def __init__(self, api_key, app_id):self.api_key = api_keyself.app_id = app_idself.base_url = "http://localhost/v1"def ask(self, question):endpoint = f"{self.base_url}/workflows/run"headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.api_key}","Content-Type": "application/json"}payload = {"app_id": self.app_id,"inputs": {"user_query": question}}response = requests.post(endpoint, headers=headers, json=payload)return response.json()["outputs"]["formatted_response"]# Usageassistant = DifyDocAssistant("your-api-key", "your-app-id")answer = assistant.ask("How do I set up authentication?")print(answer) -
JavaScript/Node.js Integration
const axios = require('axios');class DifyAssistant {constructor(apiKey, appId) {this.apiKey = apiKey;this.appId = appId;this.baseUrl = 'http://localhost/v1';}async ask(question) {try {const response = await axios.post(`${this.baseUrl}/workflows/run`,{app_id: this.appId,inputs: { user_query: question }},{headers: {'Authorization': `Bearer ${this.apiKey}`,'Content-Type': 'application/json'}});return response.data.outputs.formatted_response;} catch (error) {console.error('Error:', error);throw error;}}}// Usageconst assistant = new DifyAssistant('your-api-key', 'your-app-id');const answer = await assistant.ask('What are the API rate limits?');console.log(answer);
Step 5: Advanced Features
-
Hybrid Search Implementation
Add a code node for enhanced retrieval:
def hybrid_search(query, knowledge_base):# Semantic searchsemantic_results = knowledge_base.semantic_search(query, top_k=10)# Keyword searchkeyword_results = knowledge_base.keyword_search(query, top_k=10)# Combine and rerankcombined = merge_results(semantic_results, keyword_results)return rerank_with_model(combined, query, "RelaxAI-DeepSeek-R1")[:5] -
Conversation Memory
Add conversation tracking:
Node Type: Variable AssignerOperation: Store conversationVariables:conversation_history:- query: {{user_query}}- response: {{llm_response}}- timestamp: {{current_timestamp}}Storage: Redis cache (30-minute TTL) -
Query Expansion
Improve retrieval accuracy:
def expand_query(original_query):prompt = f"Generate 3 alternative phrasings for: {original_query}"expanded = llm_call("RelaxAI-Llama-4-Maverick", prompt, temperature=0.7)return [original_query] + expanded.split('\n')
Performance Optimization Tips
- Caching: Enable response caching for frequent queries
- Batch Processing: Process multiple documents in parallel during ingestion
- Model Selection: Use RelaxAI-DeepSeek-R1 for reranking, Llama-4-Maverick for generation
- Chunk Size: Experiment with 300-700 tokens based on your content type
- Retrieval Settings: Adjust Top K and threshold based on document corpus size
Monitoring and Analytics
Track these metrics for continuous improvement:
Retrieval Metrics: - Average retrieval score - Query success rate - Document coverage
Generation Metrics: - Response time - Token usage per query - User satisfaction scores
System Metrics: - API latency - Cache hit rate - Error rateThis example demonstrates the power of combining Dify’s visual workflow builder with RelaxAI’s models to create production-ready AI applications without extensive coding.